If your car suddenly shows a powertrain malfunction warning, it means something is wrong with the system that moves your vehicle, including the engine, transmission, and drivetrain. This message shouldn't be ignored, as it often points to issues that can lead to reduced performance or complete breakdown if not addressed promptly.
What Is a Powertrain System and Why It Matters
A powertrain is the group of components that generates power and delivers it to the wheels. It includes:
- Engine - Generates power through combustion or electric motors.
- Transmission - Controls energy delivery and gear ratios for optimal performance.
- Differential - Distributes power between wheels during turns.
- Axle assemblies - Transfer energy from the differential to the wheels.
- Driveshaft - Connects transmission to differential in rear-wheel drive cars.
What Does a Powertrain Failure Mean?
What is a powertrain malfunction? A powertrain system failure indicates your car's performance delivery system isn't functioning properly. This causes reduced performance, unusual noises, or complete loss of power.
Most Common Causes of Powertrain Faults
Powertrain malfunction issues stem from mechanical wear, electrical problems, or inadequate maintenance practices.
Mechanical Problems
Physical component issues often develop gradually. However, sudden powertrain malfunction symptoms are frequently evident. Regular care help prevent many mechanical issues.
E.g., heat poses significant risks to motor components and causes faster wear. Avoid high-performance applications where extreme operating conditions increase the cost of repairs.
- Worn bands or clutches - Cause slipping and poor acceleration.
- Damaged axle joints - Create clicking noises and vibrations during turns.
- Failing differential components - Result in grinding sounds and handling problems.
- Low transmission fluid levels - Heat internal damage.
- Contaminated lubrication - Accelerates wear on moving parts.
Manual transmission vehicles require individual maintenance procedures. Being aware of your specific transmission type assists in ensuring proper care. Technicians at reputable shops have the necessary expertise. It is them who can handle complex motor and transmission diagnosis.
Manual systems also require specific lubrication and maintenance schedules that differ from automatic system requirements.
Sensor and Electrical Failures
Modern cars rely heavily on electronic networks. Monitoring performance is the process directly linked to digital elements. Your car's computer cannot properly manage motor operations when sensors fail. This, in turn, leads to glitches.
| Component | Common Signs | Impact on Performance |
| Oxygen Sensors | Poor fuel economy, rough idle | Reduced performance, increased emissions |
| Transmission Speed Sensors | Harsh shifting, stuck in gear | The transmission may not shift properly |
| Throttle Position Sensor | Erratic acceleration, stalling | Engine response becomes unpredictable |
| Mass Airflow Sensor | Hesitation during acceleration | The engine runs rich or lean |
Studies show that 35% of issues originate from faulty sensors rather than mechanical failures in modern cars.
Symptoms of a Powertrain Malfunction

Recognizing early signs helps you address problems before they cause extensive damage to vital motor and transmission components. Your car will typically display multiple symptoms when experiencing malfunction issues.
- Warning light illumination - Dashboard displays engine indicators.
- Unusual noises - Grinding, whining, or clicking sounds from the engine or transmission areas.
- Vibrations - Excessive shaking during acceleration or at idle.
- Poor acceleration - Reduced performance affecting car operation.
- Shifting problems - Difficulty changing gears or staying stuck in gear position.
- Burning odors - Overheated parts or low transmission fluid levels create potential fire hazards.
Powertrain Light vs. Check Engine Light
While both indicators serve different purposes, understanding the distinction helps you prioritize repairs appropriately and determine repair cost expectations. The wrench icon typically represents more serious issues requiring immediate attention.
| Aspect | Powertrain | Check Engine |
| Appearance | Wrench icon or "POWERTRAIN" text | Engine-shaped symbol |
| Urgency | Immediate attention required | Can vary from minor to severe |
| Scope | The entire engine and transmission network | Primarily engine-related issues |
| Driving Safety | Often unsafe to continue driving | It may be safe for short distances |
| Common Causes | Transmission failures, axle problems | Emissions, fuel delivery, and ignition |
| Repair Cost | Typically higher ($1,500-$5,000) | Variable ($100-$2,000) |
How to Diagnose a Powertrain Fault
Proper diagnosis prevents unnecessary repairs. It ensures you fix the actual problem affecting your engine and transmission network. Professional diagnostic equipment provides accurate information about failures that have happened in your vehicle. Don't hesitate to determine the most cost-effective and high-quality repair approach.
When major issues have happened, experienced technicians can fix them efficiently. They help ensure your warranty remains intact.
- Connect the OBD-II scanner - Retrieve diagnostic trouble codes from the vehicle computer.
- Check fluid levels - Inspect transmission and engine oil.
- Visual inspection - Look for leaks or worn parts throughout the network.
- Test drive evaluation - Note specific symptoms and when they occur.
- Professional diagnosis - Have qualified technicians perform comprehensive testing to start proper repairs.
Learning to identify transmission types in your car ensures proper procedures are followed during diagnosis. After getting your car after a tune-up, monitor performance improvements and note any persistent symptoms that may indicate underlying issues requiring further attention from responsible repair professionals.
What NOT to Do When a Powertrain Failure Appears
Improper responses to engine and transmission problems can increase the cost significantly. Avoid these common mistakes when your car experiences a malfunction to prevent additional expenses. Specific messages displayed on your dashboard provide valuable information about engine and transmission health.
- Don't ignore warning lights - Continuing to drive can cause catastrophic harm requiring expensive engine or transmission replacement.
- Don't attempt complex repairs yourself - Modern cars require specialized tools and technical knowledge.
- Don't add random fluids - Wrong fluid types can damage internal parts and void warranty protection.
- Don't clear codes without fixing problems - The underlying issue will persist and may worsen over time.
- Don't delay professional service - Early intervention prevents expensive repairs and helps avoid warranty issues before major elements need to be replaced.

Choosing between independent shops and a dealership is a vital task. It affects warranty coverage and repair prices.
Consider your vehicle's warranty status. Save yourself from major repairs. Have some critical elements been replaced under warranty? In this case, ensure proper documentation. This will maintain warranty protection.
Vehicle Types Most Affected by Powertrain Faults
High-performance cars experience malfunctions more frequently. This particularly concerns models with complex all-wheel-drive systems. Electric car powertrain configurations also face challenges with battery and motor integration.
When planning a certified pre-owned car purchase, do your best to review the specific model's history.
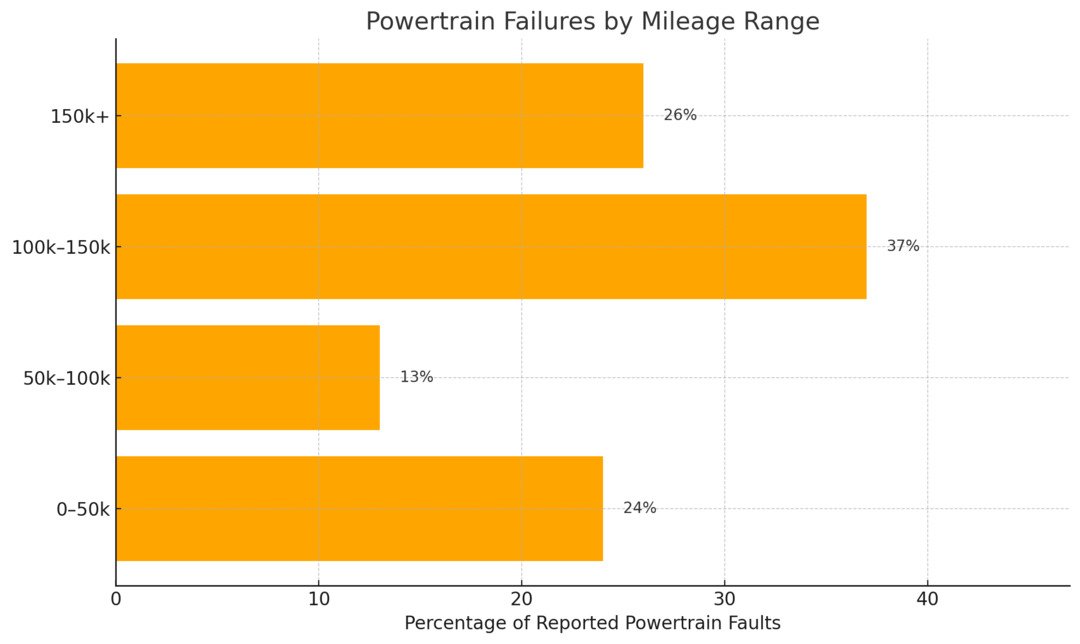
Powertrain Faults by Mileage
Different engine and transmission parts typically fail at predictable intervals. They are typically linked to vehicle usage and maintenance history.
High-mileage vehicles require more frequent inspection of transmission and axle parts. The goal is to identify early signs of wear.
- 0-50,000 - Sensor glitches, warranty-covered defects, early signs of wear.
- 50,000-100,000 - Service needs, axle joint replacement.
- 100,000-150,000 - Major repairs.
- 150,000+ - Engine rebuilds, complete replacement consideration.
EpicVIN analysis shows that most powertrain failures occur after 100,000 miles, with nearly 37% of all reported faults falling in the 100k–150k range. Early issues like sensor glitches appear below 50k miles, while full engine rebuilds are more common past 150k.
Using a VIN decoder helps identify specific maintenance schedules for your model. Vehicles accumulate distance. Parts experience normal wear patterns. Responsible owners should address specific issues promptly.
Powertrain Warranty: What’s Covered and What’s Not
Most automakers provide extensive powertrain warranty coverage. However, understanding limitations helps avoid unexpected expenses. Coverage varies significantly between manufacturers and different car body types.
Automakers typically set specific warranty conditions and features. The goal is to determine all the peculiarities of warranty coverage. Responsible vehicle owners should review their warranty terms carefully.
| Covered Components | Typical Coverage Period | Not Covered |
| Engine block and internals | 5-10 years/60,000-100,000 miles | Spark plugs, filters, and fluids |
| Transmission case and internals | 5-10 years/60,000-100,000 miles | External coolers, mounts |
| Differential assembly | 5-10 years/60,000-100,000 miles | Axle boots, CV joints |
| Transfer case (AWD) | 5-10 years/60,000-100,000 miles | Electronic controls |
Summary
Powertrain malfunction indicators require immediate attention. Understanding common causes, symptoms, and proper diagnostic procedures helps prevent severe damage to your motor system. A vehicle history report successfully reveals previous repairs. Being responsible for proper maintenance is the best job you can do.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. Severely worn spark plugs can trigger powertrain malfunction indicators. They cause misfires affecting engine performance. Check your vehicle's maintenance schedule and replace spark plugs.
Resetting the control module requires specific procedures. Always address underlying issues before attempting resets.
- Disconnect battery - Remove negative terminal for 15 minutes.
- Use diagnostic scanner - Follow manufacturer-specific reset procedures.
- Professional maintenance - Have a dealership or a qualified shop perform a reset.
Generally, no. However, driving with active problems may violate emissions regulations. Moreover, it creates safety hazards.
Yes. Powertrain problems can make the engine burn fuel poorly and harm the exhaust system. Misfires send unburned fuel into the air, broken sensors mess up fuel control, and a weak catalytic converter can’t clean the emissions well. All of this can cause your car to fail the test.
Absolutely. A loose or damaged gas cap can cause vacuum leaks. They trigger specific displays in some vehicles. Ensure your gas cap clicks securely after refueling.







