A VIN number is an identifier and the most helpful tool for learning any vehicle's past. A search of these details reveals specific information and many important facts about the history of a car. The buyers can make better choices with this information in hand. The code informs us about everything regarding a car's origin and its features. A few people only look at how nice a car appears on the outside, but using the VIN to check car history helps protect against hidden problems. A simple step keeps you away from costly mistakes, either while selling or buying cars. Definitely, you'll know what you pay for and won't get surprised later.
What Is a VIN Number?
VIN is short for Vehicle Identification Number; thus, a VIN is more like a trademark, a unique mark used on cars. This utilizes 17 symbols, both in letters and digits. The same VIN number cannot be attached to two vehicles. Every car has its digit code. At the same time, this unique identifier tells something about where this car was assembled. It refers to the model year of building a car and shows several important features of a car model. Every single digit here has some specific meaning. It also proves who the owner of the car is and that it is real when one wants to sell.
Why Decoding a VIN Number Can Save Your Money

Decoding a VIN is essential for understanding a car's complete history before purchase. A VIN decoder assists in numerous tasks:
- A thorough VIN breakdown reveals critical manufacturing details like model year and origin information, helping verify the vehicle's authenticity and specifications.
- Access to accident history and recall records through VIN decoding allows buyers to highlight potential red flags and past damage that might affect the car's value.
- Learning about a vehicle's previous use, for example, rental fleet service, empowers buyers during price negotiations.
How a VIN Number Can Reveal a Vehicle’s History
| Vehicle History Details | What the Vehicle Identification Number Tells |
| Accident Records | Shows whether the vehicle has been involved in accidents and the severity of damages reported. |
| Ownership History | Demonstrates the number of previous owners, as well as whether the car was privately owned, leased, or rented. |
| Title Status | Ensures transparency and highlights if the car has a clean title, salvage title, or other classifications. |
| Odometer Accuracy | Highlights discrepancies in reported mileage; helps detect odometer fraud. |
| Manufacturer Recalls | Demonstrates if the auto is subject to any open recalls to be addressed. |
| Country of Origin | Reveals the country where the car was manufactured, giving insights into its potential standards and quality. |
| Service and Maintenance Records | Offers access to documented repairs, inspections, and regular maintenance performed on the car. |
| Theft Records | Confirms whether the car has been reported stolen and recovered, ensuring legal ownership. |
Where Can I Find the VIN?
Knowing where's the VIN number on a car is crucial for finding car details. Here are common locations:
- Driver side doorjamb: On the sticker or plate inside the door frame.
- Windshield: A visible lower driver’s side.
- Dashboard: Near the windshield (the driver’s side).
- Engine block: Stamped on the engine itself, often near the front.
- Frame: On the chassis or frame under the car.
- Trunk: On a sticker under the spare tire or trunk lid.
- Registration documents: Printed on the vehicle's title or registration.
- Owner’s manual: Often listed in the first few pages for easy reference.
Standard vs. Hidden VIN Locations
While standard VINs are found on doorjambs, hidden car identifiers may be engraved in hard-to-reach areas like the wheel well or under the seat. These help verify authenticity during theft or fraud investigations.
Cars and Trucks
In addition to the above locations, some cars and trucks have distinctive VIN places. A code may be stamped on the radiator support, engine firewall, or even under the spare tire. This simplifies the inspection process.
Motorcycles and Scooters

Motorcycles often have VINs engraved on the steering neck or frame near the handlebars. For scooters, look for the VIN on the undercarriage or near the rear wheel housing, areas designed to be discreet yet accessible.
Classic and Vintage Cars
Vehicle identifiers on classic cars may be stamped on the engine block, front fender supports, or inside the glove compartment. Some pre-1981 models do not contain ordinary 17-symbol VINs. For such cars, additional research should be conducted.
ATVs and Off-Road Vehicles

In ATVs, these codes are typically stamped on the frame. You may sometimes find them beneath the rear fender or on the steering column. Dirt and wear can obscure them, so careful cleaning may be necessary to locate and verify these identifiers.
RVs and Trailers
RVs frequently have VINs on the driver's side dashboard, while trailers often place them on the tongue or frame near the hitch. Hidden duplicates may also exist inside cabinets or near the electrical panel.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
EV VINS are typically placed on the dashboard or doorjamb, but some are found on the battery casing. This unique location highlights the importance of the battery in defining the vehicle’s identity and specifications.
Meaning of Letters and Numbers in a VIN
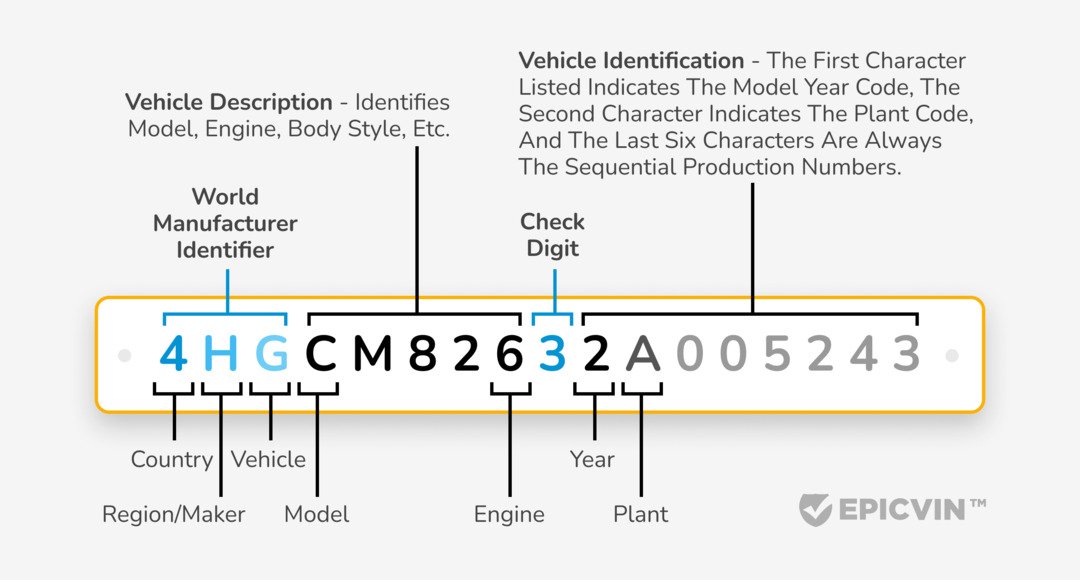
The VIN number format is a 17-character sequence designed to encode essential details about a car. From the region of production to specific manufacturing details, letters and numbers in the VIN decoding chart serve as a comprehensive identifier. Each character holds a specific meaning.
WMI (World Manufacturer Identifier)
The World Manufacturer Identifier is the first section of the VIN number structure, covering the first three characters:
- The first digit reveals the vehicle's manufacturing region. For example, a "1" indicates a U.S.-made vehicle, while a "J" signifies Japan.
- The second digit shows the manufacturer, such as Toyota, Ford, or Honda.
- The third digit specifies the type of vehicle or division within the manufacturer.
- Together, the three digits reflect the company producing the car.
Vehicle Descriptor Section (VDS)
The VDS, composed of characters 4-9, provides technical details about the car. This section usually comprises the body style, transmission style, and something about the safety systems. These alphabets and numbers help makers distinguish between model variants in combination.
For example, Ford and many others may categorize a body type as a sedan style and another as a hatchback. It holds a check digit calculated, which determines the validation procedure to make sure that no duplicate fake vehicle number is assigned, as it checks for any duplication of actual VINs.
Check Digit
The ninth character in the vehicle's VIN implies the check digit. The check digit is a security element employed in verifying the truth about a vehicle's VIN. It is computed by using a particular formula. This is an important stage when decoding or checking a VIN of a car against official records.
Vehicle Identification Section (VIS)
The last 8 characters of the VIS provide unique information about the vehicle, such as model year, assembly plant, and serial number. This section is critical in checking the make and model of a car correctly and ascertaining certain production information about the vehicle. This also helps with tracking recalls, repairs, and parts compatibility for the car.
Regional Differences in VIN
Codes on cars are unique to the specific regional regulations and standards, hence reflecting production. A truck made by a Japanese vehicle manufacturer, for example, will use different plant and emissions compliance designations than that produced in the U.S. Even the model year code may be different since this follows certain release cycles within a specific region. These variations ensure compatibility with market-specific laws, making the decoding process essential when importing or exporting vehicles across borders.
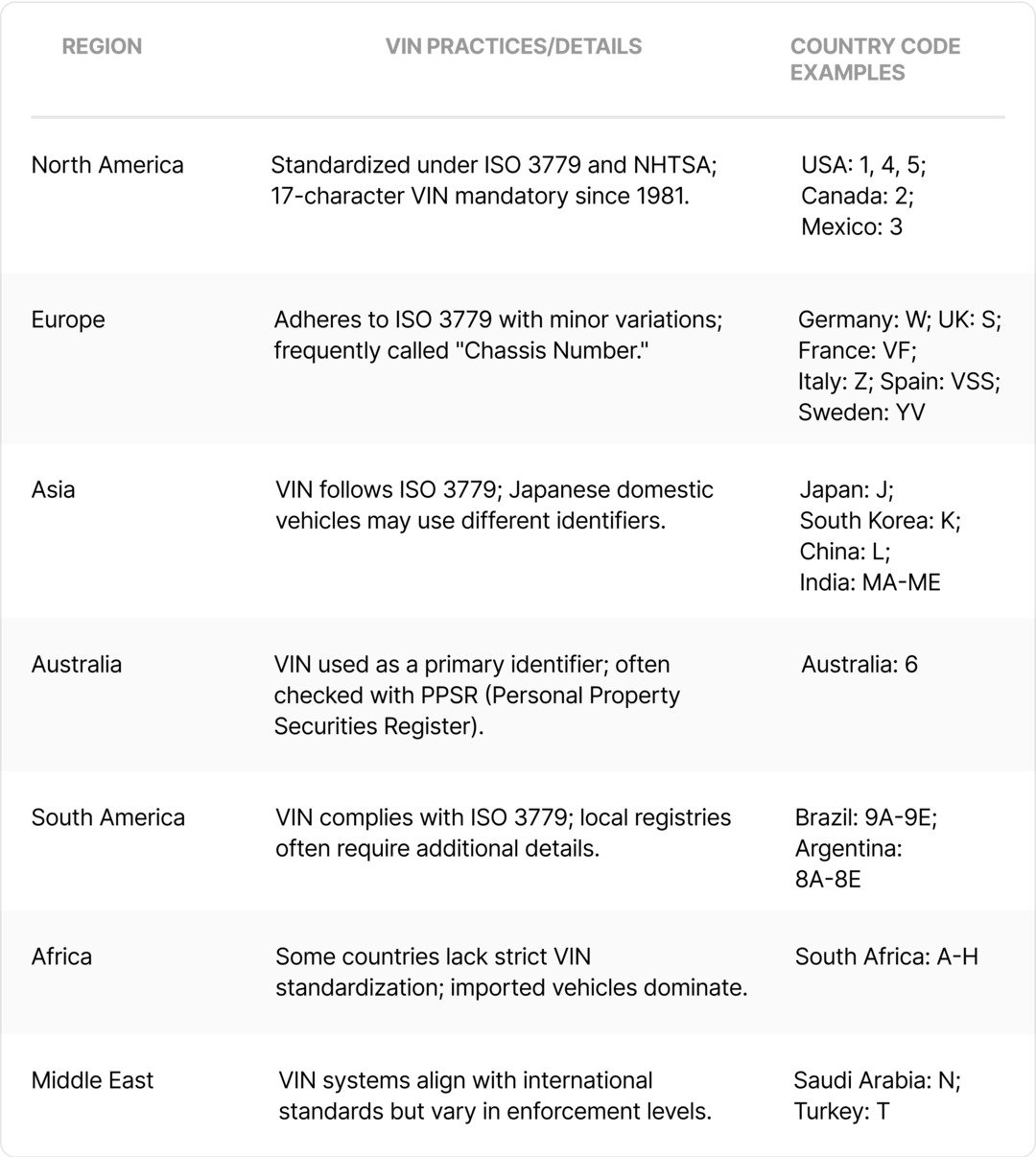
Using a VIN Decoder Tool: Tips and Tricks
Regional Specifications for Parts

VIN decoding can help you identify regional specifications for parts, which may be required for compatibility or legal reasons. Some of the key information to watch out for includes:
- Country of origin: The first digit helps determine the regional standards.
- Emission codes: Comply with EPA, Euro, or other regional guidelines.
- Part variation: It describes how headlamps, suspension, and other safety features differ between models sold in various markets.
- Special editions/trims: This confirms regional-specific trim packages or performance upgrade packages.
Insurance Classification Insights
How to Save Money on Insurance Using Your VIN?
- Accurate classification: Use the vehicle identifier to confirm your car’s true category.
- Find discounts: Certain features, like anti-theft systems encoded in this unique code, may qualify for discounts.
- Verify history: A clean VIN with no major accidents or salvage titles can reduce premiums.
- Track safety features: Highlighting features such as airbags or ABS can lower your risk profile
Tracking Exported or Reimported Vehicles
The vehicle's identifier also helps trace whether a car was exported or reimported. A code in the vehicle identifier section may show where the car was manufactured and from which plant it was originally sold. This is essential when checking for hidden issues like mismatched emissions compliance or improper registrations.
Identifying Original Paint and Trim Codes
Decoding the VIN can reveal the code for a car’s original paint and trim. This is valuable for restorations or ensuring replacement parts match the original design.
Fleet or Rental Vehicle History
The VIN can indicate if a car was part of a fleet or rental service. Details about the number of previous owners in the vehicle history help uncover such classifications. Fleet vehicles are often well-maintained but may have higher mileage, affecting resale value.
Resale Value Insights
A decoded VIN provides a transparent history, critical for assessing resale value. Factors like accidents, mileage, and fleet use all influence worth. Performing a title check by VIN ensures that hidden issues don’t undervalue or overprice the car.
Stolen Vehicle Recovery
Law enforcement and agencies use the vehicle serial number to trace stolen vehicles. Decoding the VIN helps verify ownership and ensures the motor vehicle isn’t flagged as stolen.
How to Avoid a VIN Fraud
Fraudulent activities involving a vehicle ID number can result in big financial and legal headaches. Knowing how to recognize anomalies and taking the right steps to handle them keeps your investment safe.
How to Spot a Fake VIN?
Fraudsters may attempt to falsify this unique number to hide a car's true history. Here are the indicators of the fake VIN numbers explained. Use this table for guidance:

What to Do If the VIN Is Damaged or Missing?
If the car's serial number is damaged or missing, action must be taken right away. Here's how:
- Check other places: VINs are also stamped on the chassis or other concealed areas of the automobile.
- Order a replacement: You can request a certified VIN plate replacement from the manufacturer or any of its authorized dealers.
- Detailed search of history: Conduct the car's history search by using secondary identifiers like the engine or registration number.
- Report missing VINs: When tampering or theft is suspected, inform the police.
- Suspicious cars: Never buy a car without a verified serial number unless the ownership is proven by law.
Further reading
Summary
Understanding a vehicle identification number is essential for gaining detailed insights into a car's history and specifications. By searching the 17-character code, you can determine the model, body type, and production plant. The manufacturer provides the first three characters, while the check digit ensures the VIN’s authenticity. For a driver's auto, whether it's a car, truck, or SUV, decoding reveals critical details, for example, recalls and part compatibility. Proper use safeguards buyers from fraud. Additionally, vehicles meet safety and performance norms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Car serial numbers assist in tracking vehicles damaged during natural disasters. Insurance firms frequently apply them to register total losses caused by catastrophic events. A vehicle history report often labels such automobiles as "flood-damaged" or "salvaged."
Changing a VIN number on one’s own is illegal. Such a step conceals a vehicle's true identity, which may be associated with fraud or theft. This vehicle serial number serves as the car's fingerprint, making tampering a serious offense punishable by law. To avoid tampering, manufacturers adhere to different preventive strategies. They produce tamper-resistant plates, laser etching, and hidden VIN stamps.
Counterfeit/cloned vehicles often contain duplicate VINs. In this case, a legitimate VIN is copied onto a stolen or illegally assembled car. Oversight boards and buyers utilize special databases to detect inconsistencies. These may be duplicate registrations for the same VIN across various regions.
Yes, this unique number can trace a vehicle’s journey internationally. The VIN encodes the manufacturing country and plant, while import/export records link it to its transit history.